|
Cours Probabilités. |
|
$$
\newcommand{\SetN}{\mathbb{N}}
\newcommand{\SetR}{\mathbb{R}}
\newcommand{\SetC}{\mathbb{C}}
\newcommand{\SetK}{\mathbb{K}}
\newcommand{\SetZ}{\mathbb{Z}}
\newcommand{\SetQ}{\mathbb{Q}}
\newcommand{\SetU}{\mathbb{U}}
\newcommand\ds[0]{\displaystyle}
\newcommand\PCar[1]{\large{\chi}_{#1}}
\newcommand{\=}{\:=\:}
\newcommand\tendvers[2]{\displaystyle\mathop{\longrightarrow}_{#1\rightarrow#2}}
\newcommand\tr[0]{\:^t\!}
\newcommand\limite[2]{\displaystyle\mathop{\text{lim}}_{#1\rightarrow#2}\:}
\newcommand\Sup[1]{\displaystyle\mathop{sup}_{#1}}
\newcommand\Inf[1]{\displaystyle\mathop{inf}_{#1}}
\newcommand\Haut[1]{}
\newcommand\vect[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}}
\newcommand\tendversCU[0]{\:\displaystyle\mathop{\Large\longrightarrow}_{n\rightarrow+\infty}^{_{CU}}\:}
\newcommand\tendversCS[0]{\:\displaystyle\mathop{\Large\longrightarrow}_{n\rightarrow+\infty}^{_{CS}}\:}
\newcommand\tendversCN[0]{\:\displaystyle\mathop{\Large\longrightarrow}_{n\rightarrow+\infty}^{_{CN}}\:}
\newcommand\tendversCUS[0]{\:\displaystyle\mathop{\Large\longrightarrow}_{n\rightarrow+\infty}^{_{CUS}}\:}
\newcommand\tendversNorme[1]{\:\displaystyle\mathop{\Large\longrightarrow}_{n\rightarrow+\infty}^{#1}\:}
\newcommand\simL[0]{\displaystyle\mathop{\sim}_{^{^L}}}
\newcommand\simC[0]{\displaystyle\mathop{\sim}_{^{^C}}}
\newcommand\simLC[0]{\displaystyle\mathop{\sim}_{^{^{LC}}}}
\newcommand\fonction[5]{
\begin{array}{cccc}
#1\::\:& #2 & \rightarrow & #3 \\
& #4 & \mapsto & \ds #5 \
\end{array}}
$$
| Liste chapitres | Plan du chapitre |
|
|
||||||
| |||||||||
III. Variables aléatoires discrètes. III.1. Définition.
Définitions.
Programme PSI.
Il existe des variables aléatoires non discrètes, c'est-à-dire des applications dans un ensemble $F$ non dénombrable, mais c'est hors programme. Les variables aléatoires seront dorénavant des variables aléatoires discrètes.
Intérêts.
Notations.
Exemple.
On regarde la durée de vie en jours d'une ampoule fabriquée dans une usine et on considère $X$ la variable aléatoire à valeurs dans $F=\{\text{'Très bien'}, \text{'Bien'}, \text{'Passage'}, \text{'Nul'}\}$ définie par :
$$X(\omega)\=\left\{\begin{array}{lll}
\text{'Nul'}&\text{si }\omega\in[0;100[\\
\text{'Passable'}&\text{si }\omega\in[100;300[\\
\text{'Bien'}&\text{si }\omega\in[300;1000[\\
\text{'Très bien'}&\text{si }\omega\in[1000;+\infty[\\
\end{array}\right.$$
Cet exemple montre un exemple où l'univers $\Omega$ n'est pas dénombrable et pourtant la variable est discrète. Il donne également un exemple d'une variable aléatoire non réelle.
| |||||||||
III. Variables aléatoires discrètes. III.2. Loi d'une variable aléatoire.
Définitions.
Méthode.22
La loi de la variable aléatoire discrète $X$ est entièrement déterminée par :
Exemple.
On joue à pile ou face deux fois de suite. On prend $\Omega=\{F\!F,F\!P,P\!F,P\!P\}$ comme univers et on considère la variable aléatoire $X$ qui compte le nombre de Pile réalisé. On a alors $F=\{0,1,2\}$ et le schéma suivant :
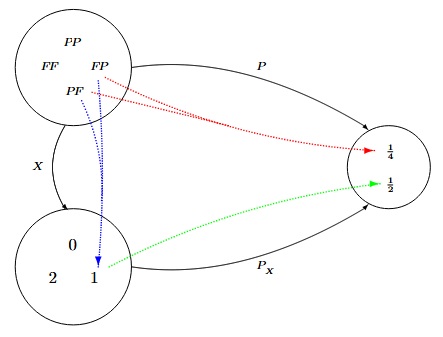
Propositions.23
Remarque.
Comme le montre la proposition 2, la loi d'une variable aléatoire ne change pas si on ajoute ou si on retire de $X(\Omega)$ des valeurs ayant une probabilité nulle. Il est donc parfois préférable lorsqu'on détermine la loi de $X$, de donner le support de $X$ au lieu de $X(\Omega)$ où :
$$\text{Supp}(X)\:\=\:\Big\{\:x\in X(\Omega)\:/\:P(X=x)>0\:\Big\}$$
Exemple.
On lance une pièce bien équilibrée jusqu'à obtenir pile. On note $X$ la variable aléatoire indiquant le rang du lancé pile. On a :
$$\left\{\begin{array}{l}
X(\Omega)\=\SetN^*\cup\{+\infty\}\\[0.1cm]
\forall k\in\SetN^*,\:P(X=k)=\left(\frac{1}{2}\right)^k\\[0.12cm]
P(X=+\infty)=0
\end{array}\right.
$$
Ici il est préférable de prendre :
$$\left\{\begin{array}{l}
Supp(X)\=\SetN^*\\[0.1cm]
\forall k\in\SetN,\:P(X=k)=\left(\frac{1}{2}\right)^k\\
\end{array}\right.
$$
| |||||||||
III. Variables aléatoires discrètes. III.3. Représentation graphique d'une variable aléatoire réelle.
Définition.
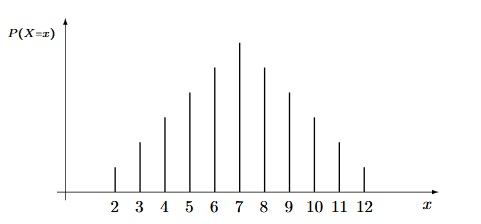
Pour représenter une variable aléatoire réelle, on utilise un diagramme en bâton. Les abscisses sont données par les valeurs $x_i$ de $X(\Omega)$ et la hauteur du bâton en $x_i$ est égale à $P(X=x_i)$.
Exemple.
On lance 2 dés à 6 faces. Notons $X$ la variable aléatoire égale à la somme des valeurs indiquées par les dés. La loi de $X$ est définie par $X(\Omega)=\{2,3,..., 12\}$ et :
$$
\begin{array}{|c|c|c|c|c|c|c|c|c|c|c|c|c|}
%\renewcommand\arraystretch{1.5}
\hline
\Haut{0.55}x&2&3&4&5&6&7&8&9&10&11&12\\[0.17cm]\hline
\Haut{0.65}P(X=x)&\frac{1}{36}&\frac{2}{36}&\frac{3}{36}&\frac{4}{36}&\frac{5}{36}&\frac{6}{36}&
\frac{5}{36}&\frac{4}{36}&\frac{3}{36}&\frac{2}{36}&\frac{1}{36}\\[0.3cm]\hline
\end{array}$$
Sa représentation graphique est :
 | |||||||||
III. Variables aléatoires discrètes. III.4. Loi conjointe de variables aléatoires discrètes
Définitions.
Soient $X_1$,..., $X_n$ des variables aléatoires définies sur $(\Omega,\mathcal{A},p)$ à valeurs respectivement dans $F_1$,...,$F_n$.
Remarque.
Puisque $X_1$, ..., $X_n$ sont discrêtes, il en est de même pour la loi conjointe $X=(X_1,...,X_n)$. Elle est donc définie par $X(\Omega)$ l'ensemble des valeurs prises par $X$ et les probabilités :
$$P\big(X=(a_1,...,a_n)\big)\:\=\:P\big(X_1=a_1\:\hbox{ et }\:X_2=a_2\:\hbox{ et }\:...\:\hbox{ et }\:X_n=a_n\big)$$
avec $(a_1,...,a_n)$ sont dans $X(\Omega)$.
Remarques - Le cas d'un couple de variable aléatoire.
Soit $X$ et $Y$ des variables aléatoires discrètes à valeurs respectivement dans $F$ et $G$.
Exercice.24
On lance 2 dés à 6 faces et on considère les va :
$$\begin{array} {ccl}%
X&:&\hbox{valeur du premier dé}\\
Y&:&\hbox{maximum des deux dés}\\
\end{array}%
$$
Déterminer la loi conjointe $(X,Y)$ et les lois marginale $X$ et $Y$. | |||||||||
III. Variables aléatoires discrètes. III.5. Opérations sur les variables aléatoires.
Définitions.
Soit $X$ une variable aléatoire à valeurs dans $F$ et $f$ une application de $F$ dans $G$ alors $f\:o\:X$ est une variable aléatoire à valeurs dans $G$. On la note $f(X)$, On dit que c'est l'image de $X$ par $f$.
Exemples.
Soient $X$ et $Y$ des variables aléatoires réelles définies sur le même univers.
| |||||||||