$$
\newcommand{\SetN}{\mathbb{N}}
\newcommand{\SetR}{\mathbb{R}}
\newcommand{\SetC}{\mathbb{C}}
\newcommand{\SetK}{\mathbb{K}}
\newcommand{\SetZ}{\mathbb{Z}}
\newcommand{\SetQ}{\mathbb{Q}}
\newcommand{\SetU}{\mathbb{U}}
\newcommand\ds[0]{\displaystyle}
\newcommand\PCar[1]{\large{\chi}_{#1}}
\newcommand{\=}{\:=\:}
\newcommand\tendvers[2]{\displaystyle\mathop{\longrightarrow}_{#1\rightarrow#2}}
\newcommand\tr[0]{\:^t\!}
\newcommand\limite[2]{\displaystyle\mathop{\text{lim}}_{#1\rightarrow#2}\:}
\newcommand\Sup[1]{\displaystyle\mathop{sup}_{#1}}
\newcommand\Inf[1]{\displaystyle\mathop{inf}_{#1}}
\newcommand\Haut[1]{}
\newcommand\vect[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}}
\newcommand\tendversCU[0]{\:\displaystyle\mathop{\Large\longrightarrow}_{n\rightarrow+\infty}^{_{CU}}\:}
\newcommand\tendversCS[0]{\:\displaystyle\mathop{\Large\longrightarrow}_{n\rightarrow+\infty}^{_{CS}}\:}
\newcommand\tendversCN[0]{\:\displaystyle\mathop{\Large\longrightarrow}_{n\rightarrow+\infty}^{_{CN}}\:}
\newcommand\tendversCUS[0]{\:\displaystyle\mathop{\Large\longrightarrow}_{n\rightarrow+\infty}^{_{CUS}}\:}
\newcommand\tendversNorme[1]{\:\displaystyle\mathop{\Large\longrightarrow}_{n\rightarrow+\infty}^{#1}\:}
\newcommand\simL[0]{\displaystyle\mathop{\sim}_{^{^L}}}
\newcommand\simC[0]{\displaystyle\mathop{\sim}_{^{^C}}}
\newcommand\simLC[0]{\displaystyle\mathop{\sim}_{^{^{LC}}}}
\newcommand\fonction[5]{
\begin{array}{cccc}
#1\::\:& #2 & \rightarrow & #3 \\
& #4 & \mapsto & \ds #5 \
\end{array}}
$$
| Liste chapitres |
Plan du chapitre |
 | Section |  |
|
 | sous-section |  |
|
|
|
| Ici sera la liste des chapitres !!! |
|
IV. Projections et symétries orthonormales.
IV.1. Unicité du supplémentaire orthogonale, à défaut de l'existence.
Définition.
Soit $F$ un sous-espace vectoriel d'un espace préhilbertien réel $E$. Un supplémentaire orthogonal de $F$ dans $E$ est un sous-espace vectoriel $G$ vérifiant : $$\ds E\=F\mathop{\oplus}^\perp G$$
Théorème - Unicité et condition d'existence. 32
Soit $(E,\left<\:,\:\right>)$ un espace vectoriel pré-hilbertien réel, et $F$ un sev de $E$.
- $F^\perp$ est le seul supplémentaire orthogonal possible de $F$ dans $E$. En d'autres termes, s'il existe $G$ vérifiant $E=F\ds\mathop{\oplus}^\perp G$ alors $G=F^\perp$.
- $F^\perp$ n'est pas toujours un supplémentaire orthogonal de $F$ c'est-à-dire que $\ds F\mathop{\oplus}^\perp F^\perp$ n'est pas toujours égal à $E$.
- Si $F$ est de dimension finie alors $E\ds=F\mathop{\oplus}^\perp F^\perp$
Le point 1 montre que le supplémentaire orthogonal d'un sev s'il existe est unique. Mais le point 2 montre qu'il n'existe pas toujours. On pourra voir un contre-exemple à la fin du paragraphe.
Exemples.
- On a : $\:\:\mathcal{S}_n(\SetR)^\perp=\mathcal{A}_n(\SetR)\:\:$ et $\:\:\mathcal{A}_n(\SetR)^\perp=\mathcal{S}_n(\SetR)\:\:$ dans $\:\mathcal{M}_{n}(\SetR)$.
- On a : $\:\:\mathcal{P}([-a,a],\SetR)^\perp=\mathcal{I}([-a,a],\SetR)\:\:$ et $\:\:\mathcal{I}([-a,a],\SetR)^\perp=\mathcal{P}([-a,a],\SetR)\:\:$ dans $\:C^0([-a,a],\SetR)$.
Remarques.
- Comme le montre les exemples précédentes, il n'y a pas de réciproque au point 3 du théorème.
- Dans une espace de Hilbert, on peut montrer que si $F$ est fermé alors $E\ds=F\mathop{\oplus}^\perp F^\perp$ ce qui généralise le point 3 du théorème.
Exercice - Un cas où le supplémentaire orthogonal n'existe pas. 33
On identifie polynôme et fonction polynôme, on peut donc supposer $\SetR[X]$ sev de $C^0([a,b],\SetR)$.
- En utilisant que toute fonction continue sur un segment est limite uniforme de polynômes, montrer que $$\SetR[X]^{\perp}=\{0\}$$
- En déduire que l'on peut trouver $F$ sev d'un $\SetR$-ev $E$ tels que $E\neq F\oplus F^{\perp}$.
- En déduire que l'on peut trouver $F$ sev d'un $\SetR$-ev $E$ tels que $\left(F^{\perp}\right)^{\perp}\neq F$.
|
IV. Projections et symétries orthonormales.
IV.2. Définitions
Définition.
Soit $F$ un sev d'un $\SetR$-ev tel que $\ds E=F\mathop{\oplus}^\perp F^\perp$ $($un sous espace vectoriel $F$ de dimension finie par exemple$)$.
- La projection orthogonale sur $F$ est la projection sur $F$ de direction $F^\perp$.
- La symétrie orthogonale sur $F$ est la symétrie par rapport à $F$ de direction $F^\perp$.
Remarques.
- Si $p$ est la projection orthogonale sur $F$ alors $Id-p$ est la projection orthogonale sur $F^\perp$. La projection $Id-p$ est la projection orthogonale associée à $p$.
- La projection orthogonale sur $F$ et la symétrie orthogonale par rapport à $F$ existent si et seulement si $\ds E=F\mathop{\oplus}^\perp F^\perp$. On sait déjà que c'est le cas par exemple si $F$ est de DF, mais pas uniquement.
Exercice.34
Soit $V$ un vecteur non nul de $\mathcal{M}_{n1}$. Montrer que l'endomorphisme de matrice :
$$P\=\frac{VV^T}{\|V\|^2}$$
est la projection orthogonale sur $\text{Vect(V)}$.
Exercice.35
Soit $p$ une projection d'un espace pré-hilbertien réel. Montrer que $p$ est une projection orthogonale si et seulement si : $$\forall x\in E,\:\|p(x)\|\:\leq\:\|x\|$$
Pour la réciproque, on pourra raisonner par contraposée. Pour une projection sur $F$ de direction $G$, on pourra prendre $\lambda$ dans $\SetR$ et $(x,y)$ dans $F\times G$ non orthogonaux et développer l'expression : $\|\lambda x+y\|^2-\|p(\lambda x+y)\|^2$
|
IV. Projections et symétries orthonormales.
IV.3. Comment trouver l'image par une projection ou symétrie ?
Méthodes - Comment trouver $p(x)$ ? 36
Soit $p$ la projection orthogonale de $E$ sur $F$ et $x$ un vecteur de $E$. Comment peut-on trouver $p(x)$ ?
- On peut facilement décomposer $x$ en $x=x_1+x_2$ avec $x_1$ dans $F$ et $x_2$ dans $F^\perp$. Dans ce cas $p(x)=x_1$
- Il existe une BON $(e_1,...,e_n)$ sur $F$. Dans ce cas :
$$p(x)\=\langle x,e_1\rangle e_1\:+\:\langle x,e_2\rangle e_2\:+\:...\:+\:\langle x,e_n\rangle e_n$$
- Sinon $p(x)$ est la seule solution du système :
$$\left\{\begin{array} {l}%
p(x)\:\in\: F\\
x-p(x)\:\perp\: F\\
\end{array}%
\right.$$
Méthode - Comment trouver $s(x)$ ? 37
Soient $s$ la symétrie orthogonale de $E$ par rapport à $F$, $p$ la projection orthogonale de $E$ sur $F$ et $x$ un vecteur de $E$. Comment peut-on trouver $s(x)$ ?
- On cherche $p(x)$.
- On utilise la relation $2p=s+id$
Exercice.38
Soient $\:E=C^0([-1,1],\SetR)\:$ et $\:p\:$ la projection orthogonale sur $\:F\:$ le sev des fonctions paires de $\:E$.
- Justifier l'existence de $p$.
- Déterminer l'image par $p$ de la fonction exponentielle.
Exercice.39
Notons $$\mathcal{A}=\left\{ \left(\begin{array} {ccc}%
a&b\\
b&a\\
\end{array}%
\right)\:/\:a,b\in\SetR\right\}$$
- Montrer que $\mathcal{A}$ est un sev $\mathcal{M}_{2}(\SetR)$ de dimension 2.
- Déterminer une base orthonormale de $\mathcal{A}$
- En déduire la matrice de la projection orthogonale sur $A$ dans $\beta=(E_{11}, E_{12}, E_{21}, E_{22})$.
Exercice.40
Soit $\:F:x+2y+z=0\:$ un plan de $\:\SetR^3$.
- Déterminer l'image de $(x,y,z)$ par $p$ la projection orthogonale sur $F$
- En déduire la matrice de $\:p\:$ dans la base canonique.
|
IV. Projections et symétries orthonormales.
IV.4. Théorème de projection.
Définition.
Soit $E$ un préhilbertien réel, $F$ un sev de $E$ et $x$ un vecteur de $E$, alors la distance de $x$ à $F$ est obtenu par :
$$d(x,F)\:\=\:\text{inf }\big\{\,d(x,y)\:/\:y\in F\,\big\}\:\=\:\text{inf }\big\{\,\|x-y\|\:/\:y\in F\,\big\}$$
Théorème.41
Soit $E$ un préhilbertien réel, $F$ un sev de $E$ et $x$ un vecteur de $E$. On suppose de plus que
$\ds E=F\mathop{\oplus}^\perp F^\perp$ pour avoir l'existence de $p$ la projection orthogonale sur $F$, alors :
$$d(x,F)\=d(x,p(x))\=\|x-p(x)\|$$
Remarques.
- L'inf de la définition de $d(x,F)$ est en fait un min puisqu'elle est atteinte pour $p(x)$.
- La meilleure approximation de $x$ par un élément de $F$ est $p(x)$.
Conséquences.42
Soient $E$ un eve, $\beta$ une BON de $E$ et $y$, $a$ des vecteurs de coordonnées $(y_1,...,y_n)$ et $(a_1,...,a_n)$ dans~$\beta$.
- Notons $H$ un hyperplan d'équation $a_1x_1+...+a_nx_n=0$ dans $\beta$, alors :
$$d(y,H)\=\frac{|\:a_1y_1+...+a_ny_n\:|}{\|a\|}$$
- Notons $D=Vect(a)$ alors :
$$d(y,D)\=\frac{\sqrt{\|y\|^2\|a\|^2-\langle a,y\rangle ^2}}{\|a\|}$$
Remarque.
Il ne faut pas apprendre les formules mais savoir les retrouver. Tout se voit sur le dessin suivant :
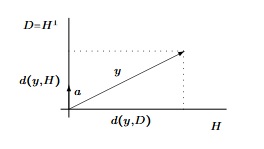
Exercice.43
Déterminer la distance entre un vecteur $\vect{u}(3,4,5)$ de $\SetR^3$ et le plan $F:x+2y+z=0$.
Exercice.44
Soit $A$ dans $\mathcal{M}_{n}(\SetR)$. Déterminer la meilleure approximation $($pour la norme usuelle$)$ de $A$ par une matrice symétrique.
Exercice.45
Déterminer : $\ds\mathop{\hbox{Inf}}_{a,b\in\SetR}\:\int_{-\frac{\pi}{2}}^\frac{\pi}{2}(\sin(x)-ax-b)^2dx$
|



