|
Cours Espaces préhilbertiens réels. |
|
$$
\newcommand{\SetN}{\mathbb{N}}
\newcommand{\SetR}{\mathbb{R}}
\newcommand{\SetC}{\mathbb{C}}
\newcommand{\SetK}{\mathbb{K}}
\newcommand{\SetZ}{\mathbb{Z}}
\newcommand{\SetQ}{\mathbb{Q}}
\newcommand{\SetU}{\mathbb{U}}
\newcommand\ds[0]{\displaystyle}
\newcommand\PCar[1]{\large{\chi}_{#1}}
\newcommand{\=}{\:=\:}
\newcommand\tendvers[2]{\displaystyle\mathop{\longrightarrow}_{#1\rightarrow#2}}
\newcommand\tr[0]{\:^t\!}
\newcommand\limite[2]{\displaystyle\mathop{\text{lim}}_{#1\rightarrow#2}\:}
\newcommand\Sup[1]{\displaystyle\mathop{sup}_{#1}}
\newcommand\Inf[1]{\displaystyle\mathop{inf}_{#1}}
\newcommand\Haut[1]{}
\newcommand\vect[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}}
\newcommand\tendversCU[0]{\:\displaystyle\mathop{\Large\longrightarrow}_{n\rightarrow+\infty}^{_{CU}}\:}
\newcommand\tendversCS[0]{\:\displaystyle\mathop{\Large\longrightarrow}_{n\rightarrow+\infty}^{_{CS}}\:}
\newcommand\tendversCN[0]{\:\displaystyle\mathop{\Large\longrightarrow}_{n\rightarrow+\infty}^{_{CN}}\:}
\newcommand\tendversCUS[0]{\:\displaystyle\mathop{\Large\longrightarrow}_{n\rightarrow+\infty}^{_{CUS}}\:}
\newcommand\tendversNorme[1]{\:\displaystyle\mathop{\Large\longrightarrow}_{n\rightarrow+\infty}^{#1}\:}
\newcommand\simL[0]{\displaystyle\mathop{\sim}_{^{^L}}}
\newcommand\simC[0]{\displaystyle\mathop{\sim}_{^{^C}}}
\newcommand\simLC[0]{\displaystyle\mathop{\sim}_{^{^{LC}}}}
\newcommand\fonction[5]{
\begin{array}{cccc}
#1\::\:& #2 & \rightarrow & #3 \\
& #4 & \mapsto & \ds #5 \
\end{array}}
$$
| Liste chapitres | Plan du chapitre |
|
|
||||||
| |||||||||
III. Utilisation et fabrication de familles orthogonales. III.1. Composantes d'un vecteur dans une BON
Théorème.24
Soient $\left(E,\langle\:,\:\rangle\:\right)$ est un eve et $\beta=(e_1,...,e_n)$ une base orthonormale de $E$. Les coordonnées d'un vecteur $x$ de $E$ peuvent être exprimées à l'aide du pse :
$$x\=\sum_{k=1}^n\langle x,e_k\rangle e_k\hskip2cm x\left(\begin{array} {c}%
\langle x,e_1\rangle \\
\langle x,e_2\rangle \\
\vdots\\
\langle x,e_n\rangle \\
\end{array}%
\right)$$
| |||||||||
III. Utilisation et fabrication de familles orthogonales. III.2. Expression du produit scalaire scalaire dans une BON
Théorème.25
Soient $E$ un eve et $\beta=(e_1,...,e_n)$ une base orthonormale de $E$. De plus notons $[x]_{_\beta}=(x_1,...,x_n)$ et $[y]_{_\beta}=(y_1,...,y_n)$ les coordonnées de $x$ et $y$ dans $\beta$, alors :
$$\langle x,y\rangle \=\left\langle [x]_{_\beta},[y]_{_\beta}\right\rangle \=\sum_{i=1}^nx_i.y_i\hskip1cm\hbox{ et }
\hskip1cm \left\|x\right\|^2\=\|[x]_{_\beta}\|^2\=\sum_{i=1}^nx_i^2$$
Dans la deuxième égalité, $\langle.\!.,.\!.\rangle$ et $\|.\!.\|$ représente le produit scalaire usuel sur $\SetR^n$ et la norme euclidienne associée.
Remarques.
| |||||||||
III. Utilisation et fabrication de familles orthogonales. III.3. Expression du projeté orthonormal dans une BON
Définition.
Soit $F$ un sev d'un $\SetR$-ev tel que $\ds E=F\mathop{\oplus}^\perp F^\perp$.
La projection orthogonale sur $F$ est la projection sur $F$ de direction $F^\perp$.
Théorème.26
Soient $E$ un pré-hilbertien réel, $F$ un sev de $E$ de dimension finie et
$(e_1,... e_n)$ une BON de $F$. Alors la projection orthogonale sur $F$ existe et :
$$p(x)\=\sum_{k=1}^n\left\langle x,e_k\right\rangle e_k$$
Remarque.
Exercice - Bessel.27
Soient $(e_n)_{_{n\in\SetN}}$ une famille orthonormale d'un espace pré-hilbertien réel.
| |||||||||
III. Utilisation et fabrication de familles orthogonales. III.4. Procédé d'orthonormalisation de Gram-Schmidt
Théorème.28
Soit $E$ un préhilbertien réel. On va décrire un procédé qui permet de construire une famille orthogonale $(o_1,o_2,...,o_n)$
à partir d'une famille libre $(l_1,l_2,...,l_n)$ de $E$. Construisons le vecteur $o_k$ par récurrence forte :
Vision géométrique de ce qu'on fait.
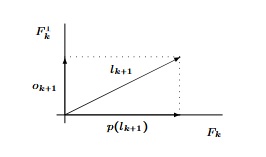
Remarques.
Propriétés.
Soit $(o_1,...,o_n)$ la famille orthogonale construite à partir de $(l_1,...,l_n)$ à l'aide du procédé de Gram-Scmidt.
Exercice.29
Soit $$\left\{\begin{array}{c}
u_1=(1,1,1) \\
u_2=(1,0,1) \\
u_3=(1,1,0) \
\end{array}\right.$$ Effectuer le procédé d'orthonormalisation de
Gram-Scmidt, afin de transformer cette famille libre en base orthonormale.
Exercice.30
On munit $\SetR_2[X]$ muni du produit
scalaire : $$(P/Q)\=\int_{-1}^1P(x)Q(x)dx$$ Utiliser l'algorithme de
Gram-Schmidt pour construire une base othogonale de polynômes unitaires à partir de la famille $\:\left(1,X,X^2\right)\:$.
| |||||||||
III. Utilisation et fabrication de familles orthogonales. III.5. Conséquences
Théorème.31
Soit $E$ un espace vectoriel euclidien $($donc de dimension finie$)$ et $F$ un sous-espace vectoriel de $E$.
| |||||||||